Capacitors Explained Types and Real Life Applications
Capacitors Explained Types and Real Life Applications , Capacitors might look like humble little components on a circuit board, but they play a surprisingly critical role in the way electronics work. From smoothing voltage to eliminating noise, capacitors act like temporary energy reservoirs that help stabilize, clean, and manage electrical signals. Understanding how they function and where they are used is essential for anyone interested in electronics, whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or seasoned engineer.
What is a Capacitor and How Does it Work?
At its core, a capacitor is an electrical component that stores and releases electrical energy. Imagine it as a short-term battery: it charges when electricity flows into it and discharges when the circuit needs that stored energy. Inside, it consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as the dielectric.
The ability of a capacitor to store charge is measured in farads (F). Though most everyday capacitors are rated in microfarads (µF) or picofarads (pF), even these tiny values have a big impact on circuit behavior.
Capacitor as a Temporary Energy Reservoir
A helpful analogy: Think of a capacitor like a sponge. When there’s too much water (voltage), it soaks some up. When water pressure drops, it squeezes some back out. This ability to buffer voltage makes it invaluable in circuits.
For example, when you’re playing music on a portable speaker, sudden changes in power demand could cause voltage drops. Capacitors step in to stabilize those changes, ensuring continuous, smooth audio playback.
Core Functions of Capacitors in Circuits
Capacitors serve various functions depending on the design of the circuit. Here are three of the most common:
1. Voltage Smoothing (Filtering)
In power supplies, capacitors are used to convert the bumpy output of rectified AC power into a smooth DC voltage. When diodes in a power supply rectify AC into DC, ripples remain. Capacitors absorb and release energy to smooth out these fluctuations.
Example: In phone chargers, capacitors ensure that your device receives a consistent voltage without damaging spikes.
2. Noise Suppression
Electrical noise can interfere with sensitive components. Capacitors help to shunt high-frequency noise to ground, effectively filtering it out.
Example: In audio amplifiers, capacitors eliminate unwanted high-frequency noise that might cause humming or buzzing in the speaker.
3. Timing and Oscillation
Together with resistors, capacitors can be used to create timing circuits. Charging and discharging patterns can control when something turns on or off.
Example: In blinking LED circuits, capacitors determine the delay between flashes.
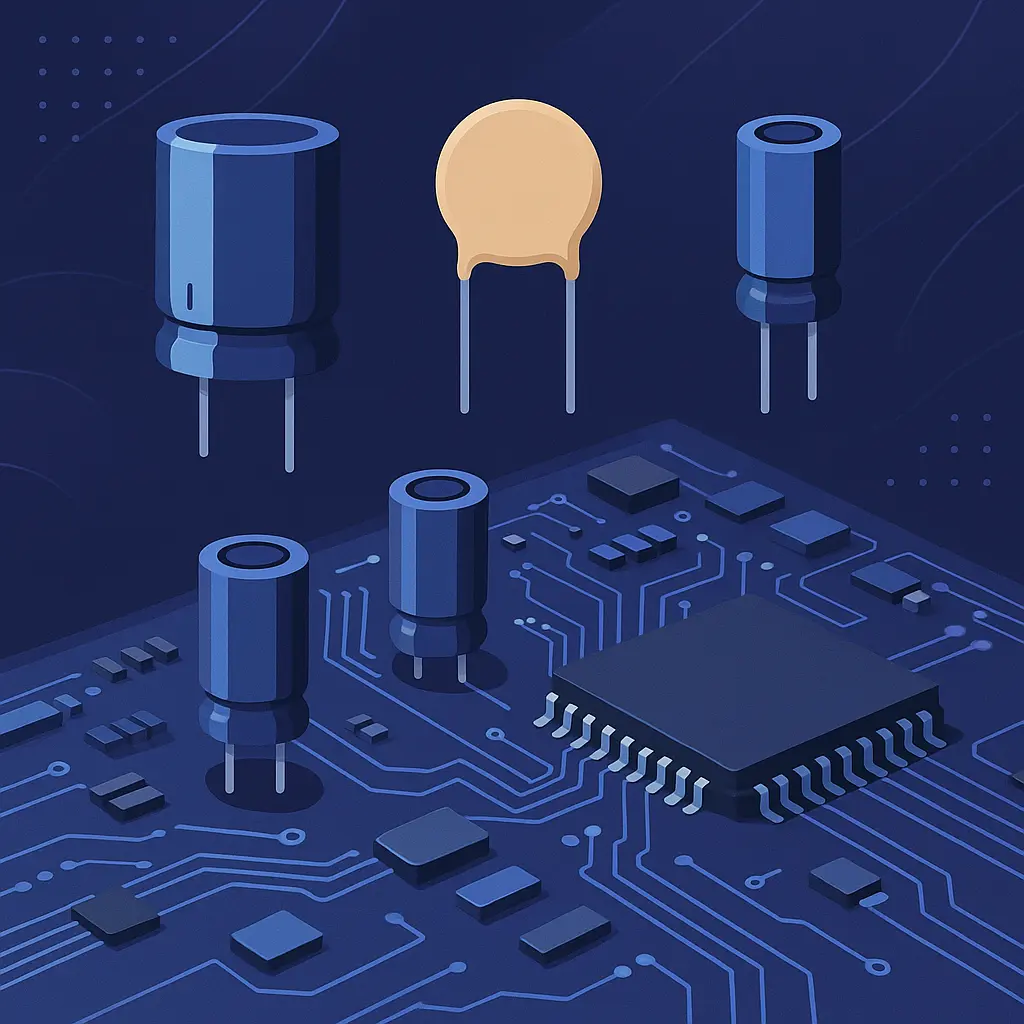
Types of Capacitors: Electrolytic vs. Ceramic vs. Tantalum
Different applications require different types of capacitors. Here’s a closer look at the three most common varieties, each with their own strengths and trade-offs.
Electrolytic Capacitors
Best for: High capacitance applications like power supply filtering.
Characteristics:
- Polarized (must be connected correctly)
- Larger physical size
- High capacitance, low cost
Real-World Example: Used in computer power supplies to handle smoothing and decoupling.
Ceramic Capacitors
Best for: High-frequency applications, decoupling, and noise filtering.
Characteristics:
- Non-polarized (can be placed either way)
- Small size, inexpensive
- Stable and reliable
Real-World Example: Found near microcontrollers on a PCB to suppress voltage spikes.
Tantalum Capacitors
Best for: Applications requiring stable capacitance and small footprint.
Characteristics:
- Polarized
- More expensive
- Stable across temperatures
- High volumetric efficiency (more capacitance in a small space)
Real-World Example: Used in smartphones and compact electronics where space and reliability matter.
| Feature | Electrolytic | Ceramic | Tantalum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polarity | Yes | No | Yes |
| Size | Larger | Very Small | Small |
| Cost | Low | Very Low | High |
| Capacitance Range | High | Low to Medium | Medium |
| Frequency Response | Poor (low freq) | Excellent (high freq) | Good |
| Stability | Moderate | Very High | High |
Visual Representation
Imagine a small PCB: right next to the microprocessor you’ll likely see a cluster of tiny beige or brown ceramic capacitors. Near the voltage regulator, the larger cylindrical cans? Those are your electrolytics. And that tiny rectangular block in your smartphone’s power section? Probably a tantalum capacitor doing some serious heavy lifting.
Real-World Example: Inside a Smartphone
Take a modern smartphone. It contains dozens of capacitors—ceramic capacitors for noise suppression, tantalums for stable power delivery, and a few electrolytics for power management. Without them, the device would either not turn on, be unstable, or emit so much noise that wireless communication would fail.
FAQs About Capacitors
Q1: Can I replace a ceramic capacitor with an electrolytic one?
Not usually. Each type is optimized for a different purpose. Ceramics handle high-frequency tasks better, while electrolytics are better for bulk energy storage.
Q2: What happens if I connect a polarized capacitor the wrong way?
It can explode or leak. Always check the polarity when dealing with electrolytic and tantalum capacitors.
Q3: Are all capacitors used for energy storage?
Yes, but in different ways. Some store energy for immediate release, others are more about maintaining signal integrity or controlling timing.
Q4: Why do some capacitors fail?
Overvoltage, aging, heat, or incorrect polarity are common reasons. Electrolytics, in particular, are more prone to aging.
Conclusion
Capacitors might seem like simple components, but their impact on modern electronics is profound. Whether you’re designing a power supply, building a radio, or repairing a smartphone, knowing your way around capacitors gives you a significant edge. From filtering and stabilizing to timing and tuning, these components are the unsung heroes of the circuit board.
If you found this article, Capacitors Explained Types and Real Life Applications, helpful, share it with your friends and visit our website for more tutorials.